Defold In-app purchase extension API documentation
This extension provides a unified, simple to use interface to several different stores for in-app purchase:
- Apple’s iOS Appstore - StoreKit
- Google Play Billing 5.0
- Amazon ‘in-app billing’ 2.0.61
- Facebook Canvas ‘game payments’
These services gives you the opportunity to sell products as:
- Standard in-app products (one time billing) of consumables or non-consumables and
- Subscriptions (recurring, automated billing)
The current Defold interface allows full interaction with Apple’s Storekit functionality. For Google Play and Facebook Canvas, the interface is identical, meaning that you can run the same code on either platform. However, some process flow might differ from platform to platform. Also note that there is currently no support for OS X purchases through the Mac Appstore.
Detailed documentation from Apple, Google, Amazon and Facebook can be found here:
- In-App Purchase Programming Guide.
- Google Play In-app Billing documentation.
- Amazon In-app Purchase documentation.
- Facebook game payments documentation.
Installation
To use this library in your Defold project, add the following URL to your game.project dependencies:
https://github.com/defold/extension-iap/archive/master.zip
We recommend using a link to a zip file of a specific release.
For Facebook Canvas you also need to add the Facebook extension as a dependency.
Testing Google Play Billing with static responses
On Android it is recommended that you start implementing IAP in your app by using static responses from Google Play. This enables you to verify that everything in your app works correctly before you publish the app. Four reserved product IDs exist for testing static In-app Billing responses:
android.test.purchased- Google Play responds as though you successfully purchased an item. The response includes a JSON string, which contains fake purchase information (for example, a fake order ID).
android.test.canceled- Google Play responds as though the purchase was canceled. This can occur when an error is encountered in the order process, such as an invalid credit card, or when you cancel a user’s order before it is charged.
android.test.refunded- Google Play responds as though the purchase was refunded.
android.test.item_unavailable- Google Play responds as though the item being purchased was not listed in your application’s product list.
Setting up your app for purchases/billing
The procedure on iOS and Android is similar:
- Make sure you are a registered Apple or Google Play developer.
- Set up your project so it works on your target device. See the iOS development and Android development guides.
-
Set up the app for testing:
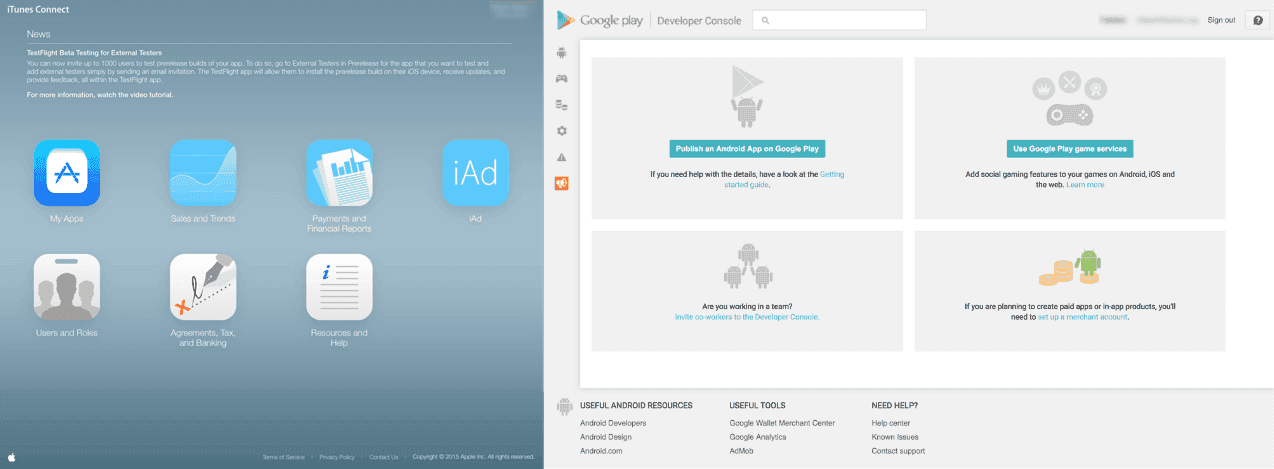
- For Android, this is done on the Google Play Developer Console.
- For iOS, this is done on iTunes Connect. Make sure that your App ID (created in the “Member Center” on https://developer.apple.com) has “In-App Purchase” enabled.
-
For Google Play, you need to upload and publish an alpha .apk file. For iTunes Connect, you should not upload the development binary to iTunes Connect until the application is ready for App Review approval. If you upload a binary to iTunes Connect and it is not fully functional, Apple will likely reject it.
-
Create products for your app.
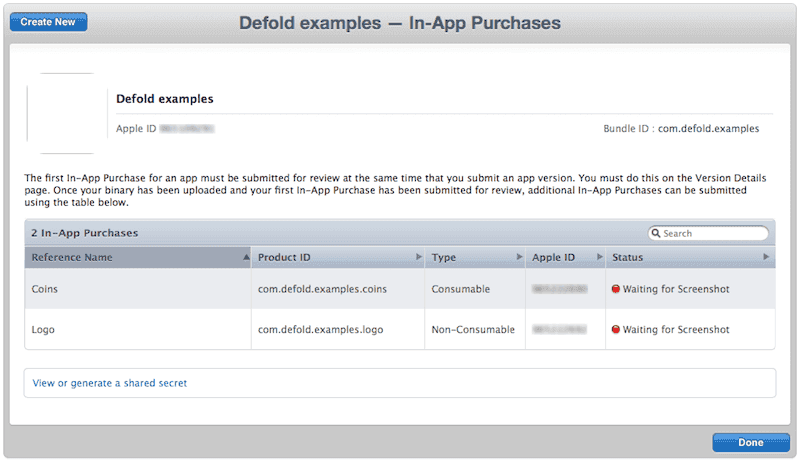
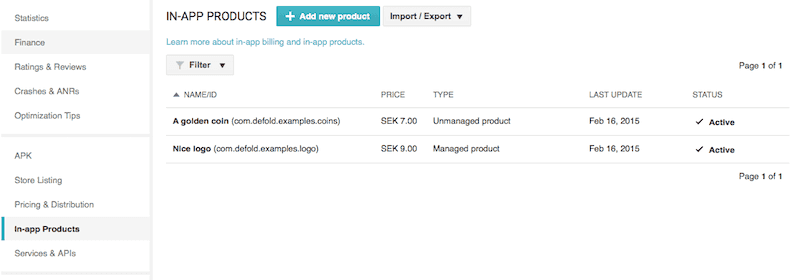
- Add test users.
- The iTunes Connect page Users and Roles allow you to add users that can do test purchases in the sandbox environment. You should sign your app with a Developer certificate and use the sandbox account in Appstore on the test device.
- From the Google Play Developer Console, choose Settings > Account Details where you can add user emails to the License Testing section. Separate the emails by commas. This allows your testers to use test purchases that don’t actually cost real money.
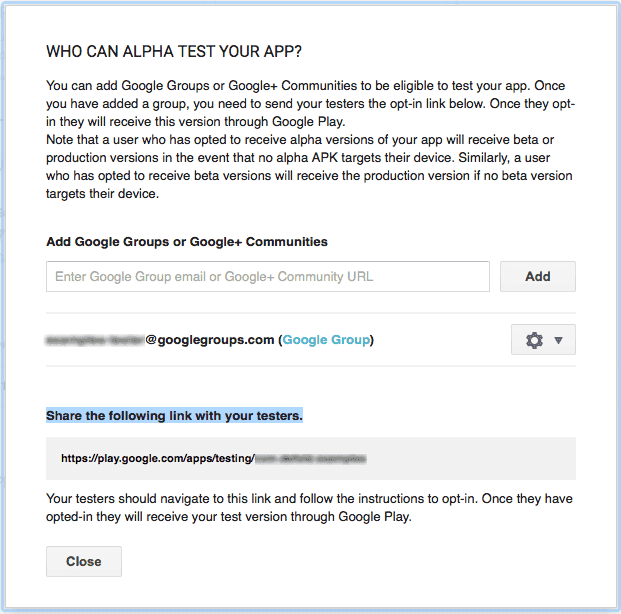
- On Google Play, you also need to set up a Google Group for your testers. Google uses Groups to manage testers that can download your app from the Alpha and Beta stores. Click on the Alpha Testing tab and then Manage list of testers to add your Google Group as Alpha testers. The app must have passed through alpha publishing before you can see the opt-in link.
The procedure on Facebook:
- Make sure you are a registered Facebook developer. Go to Facebook for developers, “My Apps” and “Register as a developer”, follow the steps.
- Facebook has extensive payment functionality and requires support of both synchronous and asynchronous payments. More info here Payment overview
- Set up app hosting and callback server:
- You will need to set up a secure canvas URL hosting your project. How this works is explained here Games on Facebook.
- The next step is to set up your callback server. Follow the steps here Setting up your callback server.
- Set up you canvas app. Follow the steps on Facebook Developer Dashboard.
- Add test users. This is done in the “Canvas Payments” section of the app dashboard.
- Create products for your app Defining products.
Asynchronous transactions
The IAP API is asynchronous, meaning that after each request that your program sends to the server, the program will not halt and wait for a response. Instead, the program continues as ordinary and when the response arrives, a callback function is invoked where you can react to the response data.
To fetch all product information available:
local COINS_ID = "com.defold.examples.coins"
local LOGO_ID = "com.defold.examples.logo"
local function product_list(self, products, error)
if error == nil then
for i,p in pairs(products) do
print(p.ident)
print(p.title)
print(p.description)
print(p.currency_code)
print(p.price_string)
end
else
print(error.error)
end
end
function init(self)
-- Initiate a fetch of products (max 20 at a time for Google Play)
iap.list({ COINS_ID, LOGO_ID }, product_list)
end
To perform actual transactions, first register a function that will listen to transaction results, then call the store function at the appropriate time:
local function iap_listener(self, transaction, error)
if error == nil then
if transaction.state == iap.TRANS_STATE_PURCHASING then
print("Purchasing...")
elseif transaction.state == iap.TRANS_STATE_PURCHASED then
print("Purchased!")
elseif transaction.state == iap.TRANS_STATE_UNVERIFIED then
print("Unverified!")
elseif transaction.state == iap.TRANS_STATE_FAILED then
print("Failed!")
elseif transaction.state == iap.TRANS_STATE_RESTORED then
print("Restored")
end
else
print(error.error)
end
end
function on_message(self, message_id, message, sender)
...
-- Register the function that will listen to IAP transactions.
iap.set_listener(iap_listener)
-- Initiate a purchase of a coin...
iap.buy(COINS_ID)
...
end
The device operating system will automatically show a pop-up window allowing the user to go through with the purchase. The interface clearly indicates when you are running in the test/sandbox environment.
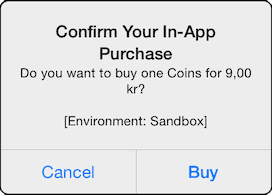
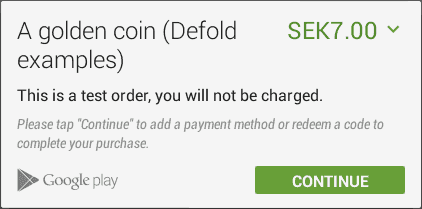
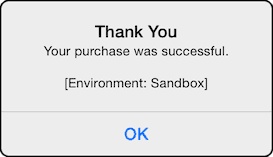
Synchronous payments
Most payment providers only supports synchronous payments. This means that the client (your application) will receive a notification when the payment is complete, TRANS_STATE_PURCHASED. This is the final state of the payment, meaning no more callbacks will be done on this transaction.
Asynchronous payments
Some payment providers require supporting asynchronous payments. This means that the client (your application) will only receive a notification when the payment is initiated. In order to verify completion of payment, further communication needs to be done between the developer server (or client) and the payment provider in order to verify.
In the case of an initiated asynchronous payment the IAP listener will receive the state TRANS_STATE_UNVERIFIED to indicate this (as opposed to TRANS_STATE_PURCHASED). This is the final state of the payment, meaning no more callbacks will be done on this transaction.
Purchase fulfilment
In order to complete a purchase from a payment provider, the application needs to signal a purchase fulfilment to the provider telling the provider the purchase has gone through (for example by developer server-side verification).
IAP supports auto-completion, where fulfilment is automatically signalled to the provider when a purchase is complete (this is the default behavior). You can also disable auto-completion in the game project settings. You are then required to call iap.finish() when the transaction is complete, which will signal purchase fulfilment to the provider.
Consumable vs non-consumable products
Google Play
It is recommended to use manual fulfilment of purchases and never finish purchases for products that should be non-consumable. As long as a purchase isn’t finished it will be returned as an active purchase when iap.set_listener() is called. If you do not call iap.finish() on a purchase you still need to indicate to Google Play that the purchase has been handled. You can do this by calling iap.acknowledge(). If you do not call iap.acknowledge() the purchase will be automatically refunded by Google after a few days.
App Store
The Apple App Store supports non-consumable products which means that you need to finish all purchases when you provide products to your users. You can do it automatically by keeping the default behavior in the game project settings or manually (if you want to do that after server validation, for example) using iap.finish().
Transaction receipt
The receipt is a signed chunk of data that can be sent to the App Store to verify that the payment was successfully processed. This is most useful when designing a store that uses a separate server to verify that payment was processed.
Differences between supported platforms
Amazon supports two different product types: subscriptions and consumable products.
Google Play and Apple supports three different product types: subscriptions, consumable and non-consumable products.
If you want to simulate non-consumable products on Amazon you need to make sure to not call iap.finish() on the product in question (and make sure to not have enabled Auto Finish Transactions in game.project).
Calls to iap.buy() and iap.set_listener() will return all non-finished purchases on Google Play. (This will not happen on iOS)
The concept of restoring purchases does not exist on Google Play/Amazon. Calls to iap.restore() on iOS will return all purchased products (and have product state set to TRANS_STATE_RESTORED). Calls to iap.restore() on Google Play will return all non-finished purchases (and have product state set to TRANS_STATE_PURCHASED).
Troubleshooting
- Android
iap.list()returns “failed to fetch product” - You need to upload and publish an .apk on the alpha or beta channels on the Google Play Developer Console. Also make sure that the time and date on your device is correct.
- Android (Google Play)
iap.list()never returns more than 20 products - Google has a limit of 20 products per request. The solution is to make multiple calls to
iap.list()and combine the results if the number of products exceeds 20. - iOS
iap.list()returns nothing - Make sure that you’ve requested an iOS Paid Applications account, and all proper documentation has been filed. Without proper authorization, your iOS app purchasing (even test purchases) will not work.
Check that the AppId you have on the “Member Center” has in-app purchases activated and that you are signing your app (or the dev-app) with a provisioning profile that is up to date with the AppId (check the “Enabled Services:” field in the provisioning profile details in the “Certificates, Identifiers & Profiles” area of “Member Center”)
Wait. It can take a few hours for the In-App product IDs to propagate to the Sandbox environment.
- iOS
iap.list()fails logging error “Unexpected callback set” iap.list()does not support nested calls. Callingiap.list()from aniap.list()callback function will be ignored, with the engine logging this error.- On iOS, the “price_string” field contains ‘~’ characters
- The ‘~’ characters are placeholders where no matching character could be found in the font file. The “price_string” field returned in the product list when using
iap.list()is formatted with a non breaking space (\u00a0) between the value and the currency denominator. If you render this string in the GUI, you need to add the character to the font’s extra_characters field. On Mac OS X you can type non breaking spaces by pressing Option + SPACE. See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-breaking_space for more information.
Source code
The source code is available on GitHub
API reference
- Defold In-app purchase extension API documentation
- Installation
- Testing Google Play Billing with static responses
- Setting up your app for purchases/billing
- Asynchronous transactions
- Synchronous payments
- Asynchronous payments
- Purchase fulfilment
- Consumable vs non-consumable products
- Transaction receipt
- Differences between supported platforms
- Troubleshooting
- Source code
- English
- 中文 (Chinese)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Νεοελληνική γλώσσα (Greek)
- Italiano (Italian)
- Język polski (Polish)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Русский (Russian)
- Українська (Ukranian)
Did you spot an error or do you have a suggestion? Please let us know on GitHub!
GITHUB