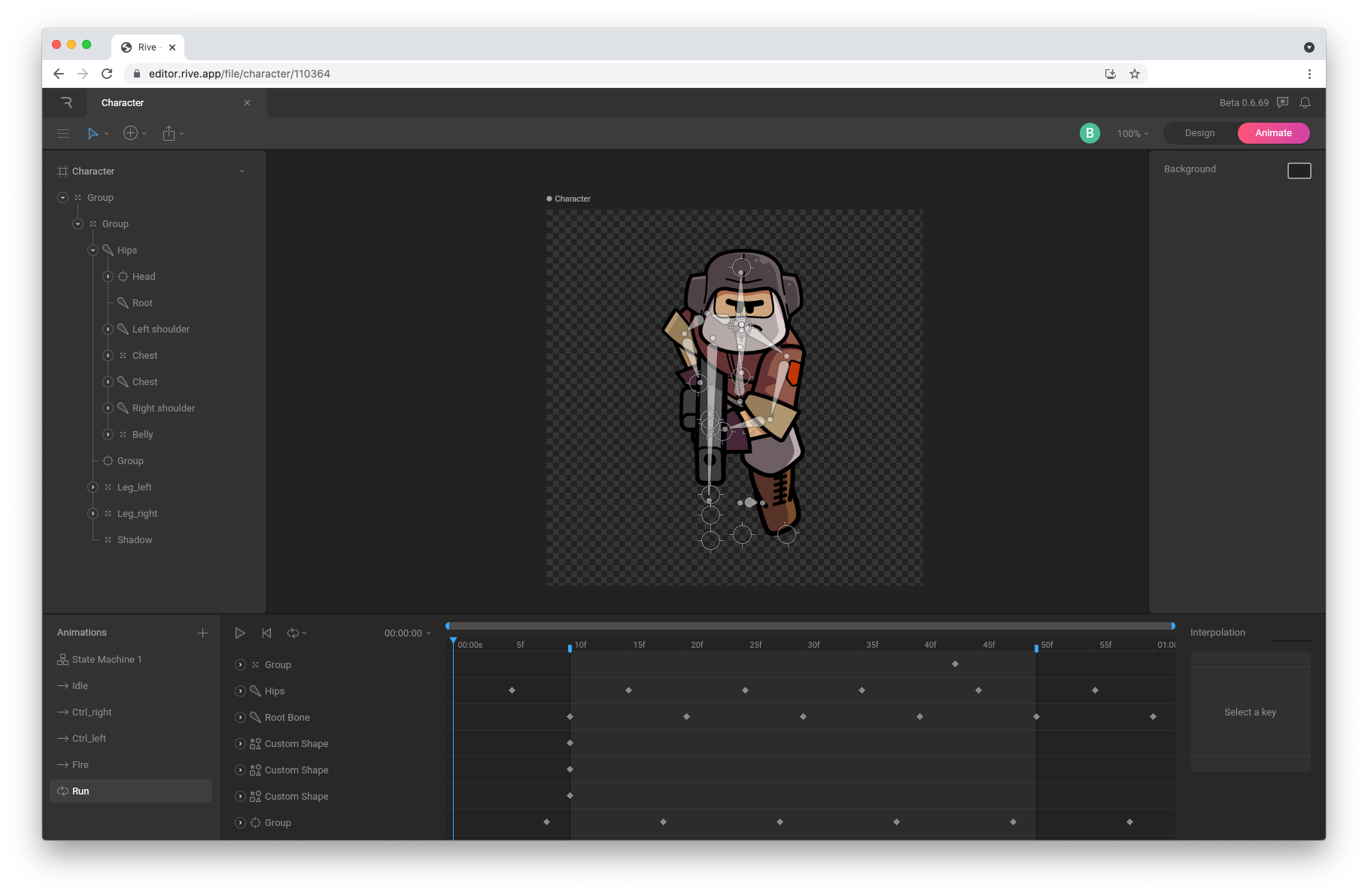
Rive animation
Rive is a real-time interactive design and animation tool by Rive Inc.. Use the Rive editor to create vector based motion graphics that respond to different states and user inputs. Rive lets you create advanced timeline animations through animation mixing, interpolation and inverse-kinematics. Transition between animations using State Machines.
Requirements
In order to use Rive content, you will need to run Defold 1.9.5 or higher.
Installation
Rive animation support in Defold is provided through an official Rive extension. To use Rive animations in a Defold project, add the following URL to the list of game.project dependencies:
https://github.com/defold/extension-rive/archive/main.zip
We recommend using a link to a zip file of a specific release.
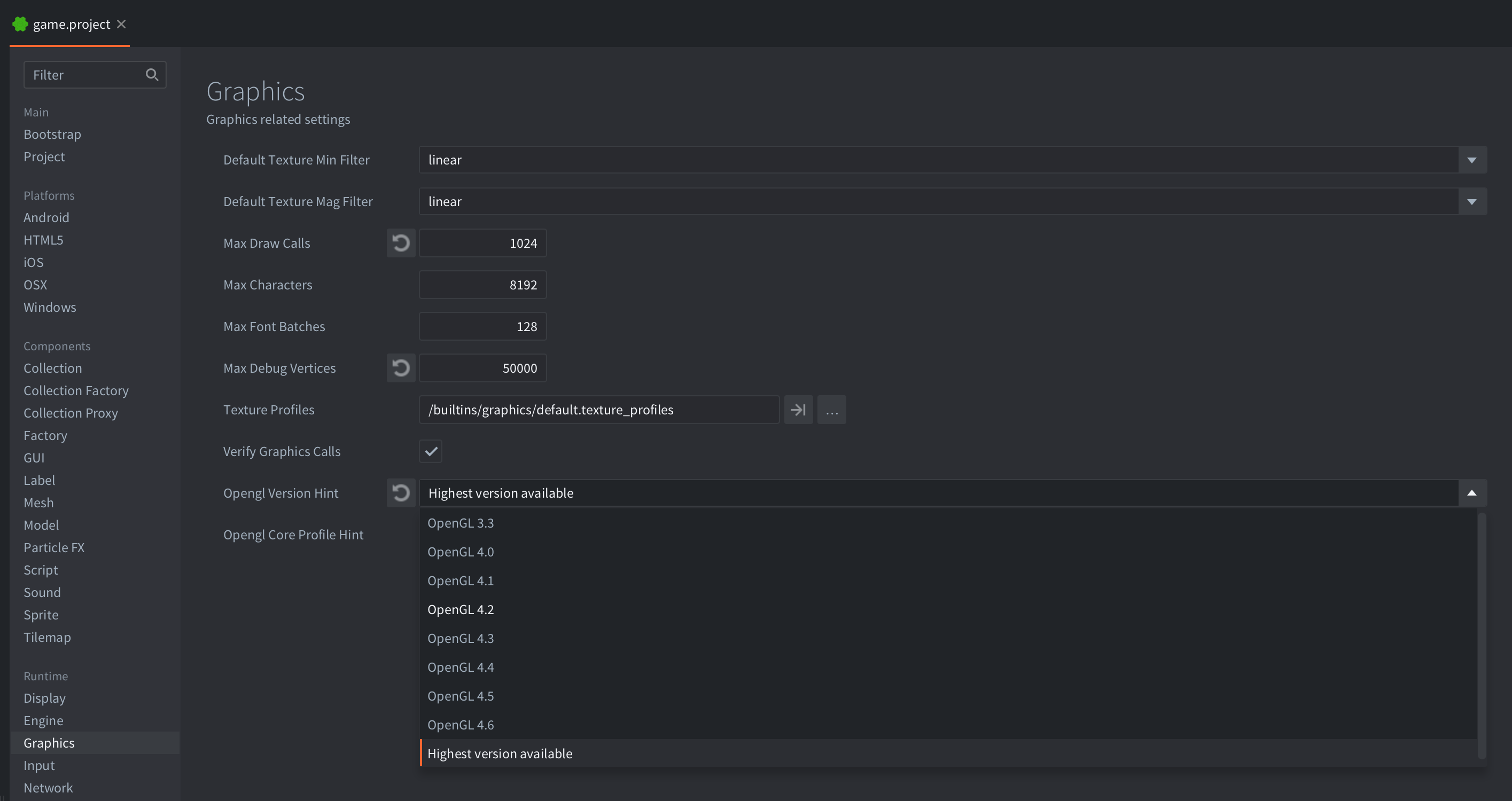
Windows
To use Rive on Windows, you need to make sure OpenGL 4.2 or later is used in the engine. To do this, set the OpenGL version hint to either 4.2 or Use highest available:
Rendering
The Rive extension is using a native renderer from the Rive runtimehttps://github.com/rive-app/rive-runtime itself by issuing raw graphics API calls behind the scenes. The low-level renderer doesn’t rasterize rive paths using regular triangles - instead a complex series of draw commands are issued that will produce smooth vector graphics. With this in mind, there are a few caveats for how the renderer works together with the regular Defold rendering.
Coordinate systems
The extension exposes two different coordinate systems that can be used to position the Rive content on screen:
- Fullscreen
- Similar to the other Defold components, Y coordinates increase upwards.
- Rive
- The Rive content will be placed according to the Rive coordinate system, where Y increases downwards from top-left. The placement can be further controlled by changing the
FitandAlignmentmodes on the Rive model component.
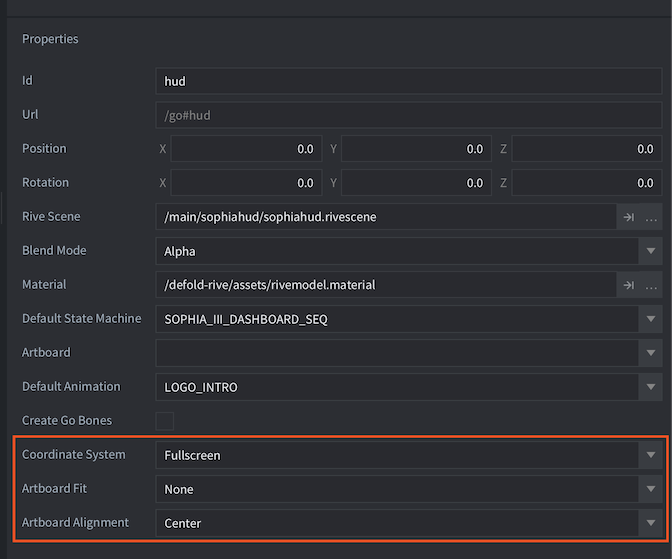
When using the Rive coordinate system, the Fit and Alignment settings affect how the Rive content is rendered.
The Fit parameter determines how the Rive content will be fitted to the view. There are a number of options available:
- Cover
- Rive will cover the view, preserving the aspect ratio. If the Rive content has a different ratio to the view, then the Rive content will be clipped.
- Contain
- (Default) Rive content will be contained within the view, preserving the aspect ratio. If the ratios differ, then a portion of the view will be unused.
- Fill
- Rive content will fill the available view. If the aspect ratios differ, then the Rive content will be stretched.
- FitWidth
- Rive content will fill to the width of the view. This may result in clipping or unfilled view space.
- FitHeight
- Rive content will fill to the height of the view. This may result in clipping or unfilled view space.
- None (default)
- Rive content will render to the size of its artboard, which may result in clipping or unfilled view space.
- ScaleDown
- Rive content is scaled down to the size of the view, preserving the aspect ratio. This is equivalent to Contain when the content is larger than the canvas. If the canvas is larger, then ScaleDown will not scale up.
The Alignment parameter determines how the content aligns with respect to the view bounds. The following options are available:
Center (Default) TopLeft TopCenter TopRight CenterLeft CenterRight BottomLeft BottomCenter BottomRight
Mixing Defold and Rive content
The Rive API does not have an exposed projection matrix that can be set, which means that in order to match the Rive coordinate space, a fullscreen projection is used in the render script.
To help with mixing Defold and Rive content, the extension provides the helper function rive.get_projection_matrix() that can be used as the projection matrix in the render script:
render.set_projection_matrix(rive.get_projection_matrix())
render.set_viewport(0, 0, render.get_window_width(), render.get_window_height())
-- The rive component and sprite components will now be in the same coordinate system,
-- as long as the coordinate system for Rive model used in the scene is set to "fullscreen"!
render.draw(self.rive_pred)
render.draw(self.sprite_pred)
If you want to mix Defold and Rive content, you will need to set the Coordinate system field on the Rive component to “Fullscreen” in order to be able to place components in the same space.
For convenience, there is a modified render script included with the projection matrix extension. Open your game.project file and modify the Render field in the Bootstrap section to use the defold-rive/lua/rive.render file from this extension.
View matrix
View matrices are supported, but only in 2D space since Rive content is essentially orthographic by design. For example, using the view matrix from a camera component can be used to implement camera effects, such as screen shakes or as a regular game camera in 2D.
Note! Support for using a view matrix / camera component to display Rive content is currently considered a work-in-progress and might not work as expected yet.
If you want to use a view matrix in 3D space, you will need to set the Coordinate system field on the Rive component to “Rive” in order to be able to place components in the same space.
Blending
Blending is currently only supported from within the .riv files themselves. Changing the blend mode on the component or the render script will have no effect.
Concepts
- Rive data file
- This file contains a Rive artboard with all of the composition and animation data of a Rive scene. You can export a Rive (.riv) file from the Rive editor.
- Rive scene
- This file is used to create a reference to a Rive data file (.riv).
- Rive model
- This file represents a Rive Model component that can be added to a game object. It references a Rive Scene, blend mode, material and the default State Machine and animation to use.
Creating a Rive scene
Create a Rive scene by (right click a location in the Assets browser, then select New... ▸ Rive Scene from the context menu). Select the Rive data file to use from the Rive File field in the Properties panel.
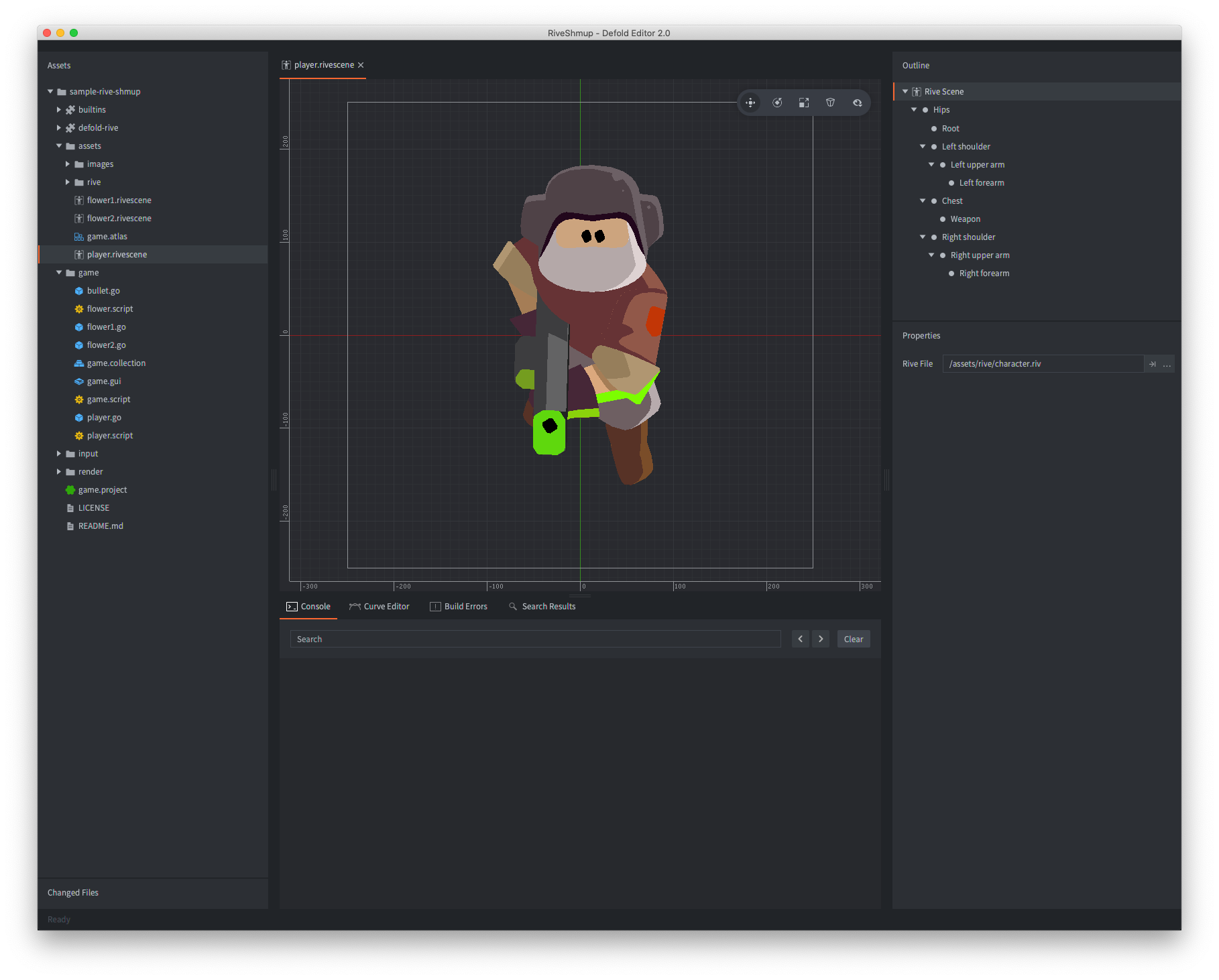
Once a Rive file has been selected a preview will be shown in the main Editor scene view and the bone hierarchy (see below) will be shown in the Outline panel.
If your Rive scene contains multiple Artboards the Rive integration in Defold will automatically select the Main Artboard from your Rive scene.
Creating Rive model components
Select a game object to hold the new component:
Either create the component in-place (right click the game object and select Add Component ▸ Rive Model)
Or create it on file first (right click a location in the Assets browser, then select New... ▸ Rive Model from the context menu), then add the file to the game object by right clicking the game object and selecting Add Component File).
The Rive model can now be viewed in the editor:
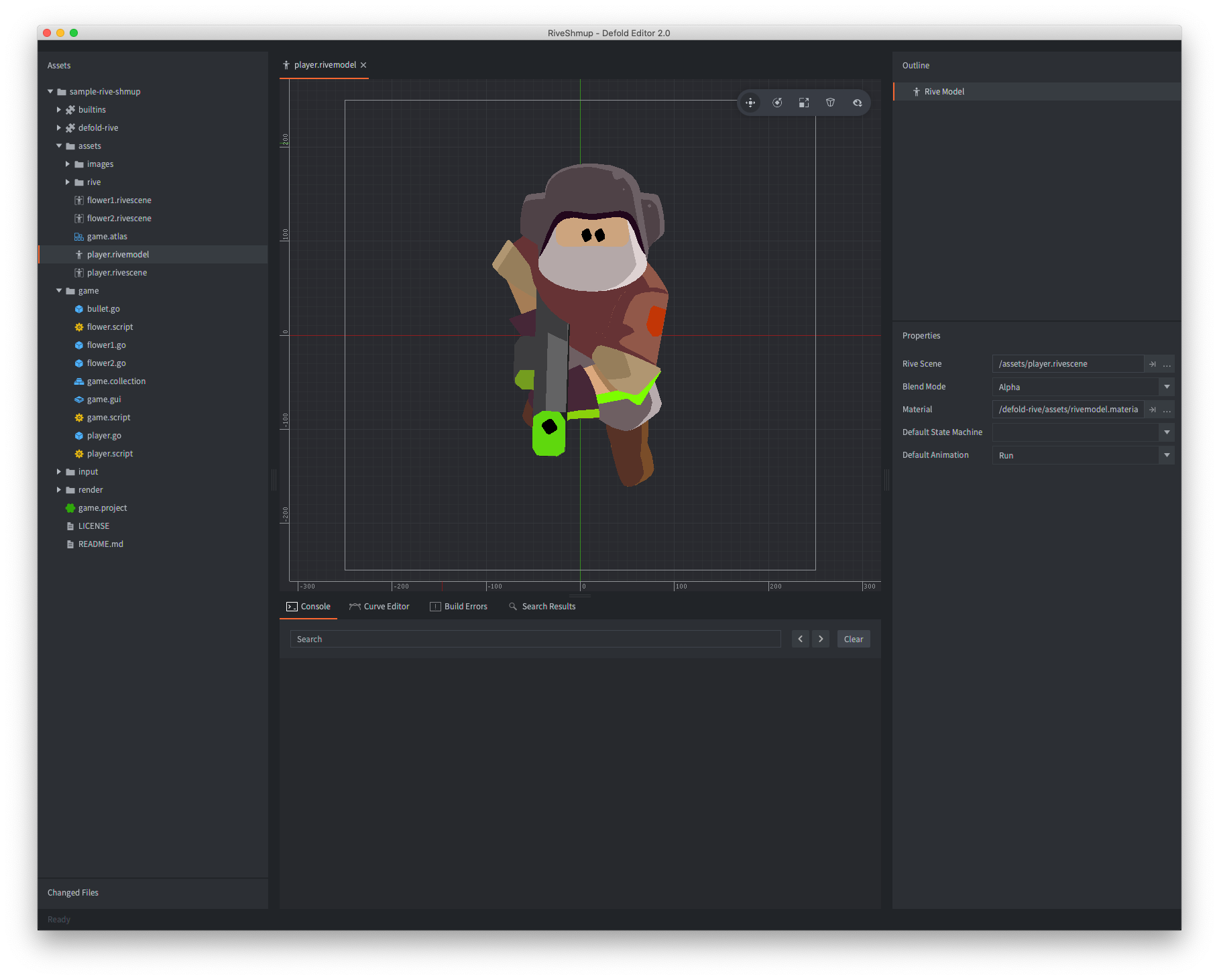
Rive model properties
Apart from the properties Id, Position and Rotation the following component specific properties exist:
- Rive Scene
- Set this to the Rive scene file to use for this model.
- Material
- If you need to render the model with a custom material, change this property.
- Default State Machine
- Set this to the State Machine you want the model to start with.
- Default Animation
- Set this to the animation you want the model to start with.
Runtime manipulation
Rive Model components can be manipulated at runtime through a number of different functions and properties (refer to the API docs for usage).
Playing animations
To play animations on a Rive Model component, simply call the rive.play_anim() function:
function init(self)
-- Play the "run" animation on the component "rivemodel"
local options = {
offset = 0.2, -- start 20% into the animation
playback_rate = 1.5, -- play the animation at 150% speed
}
rive.play_anim("#rivemodel", "run", go.PLAYBACK_ONCE_FORWARD, options, function(self, message_id, message, sender)
run()
end)
end
Cursor animation
In addition to using the rive.play_anim() to advance a Rive animation, Rive Model components expose a “cursor” property that can be manipulated with go.animate() (more about property animations):
-- Set the animation on the spine model but don't run it.
rive.play_anim("#rivemodel", "run", go.PLAYBACK_NONE)
-- Set the cursor to position 0
go.set("#rivemodel", "cursor", 0)
-- Tween the cursor slowly between 0 and 1 pingpong with in-out quad easing.
go.animate("#rivemodel", "cursor", go.PLAYBACK_LOOP_PINGPONG, 1, go.EASING_INOUTQUAD, 6)
Changing properties
A Rive Model component also has a number of different properties that can be manipulated using go.get() and go.set():
animation- The current model animation (
hash) (READ ONLY). You change animation usingrive.play_anim(). cursor- The normalized animation cursor (
number). material- The rive model material (
hash). You can change this using a material resource property andgo.set(). Refer to the API reference for an example. playback_rate- The animation playback rate (
number).
Interacting with State Machine Inputs
Inputs are used to control the transitions in a State Machine by assigning them as conditions in the Rive editor. At runtime it is possible to tie into these inputs from your game logic. In order to modify the inputs the State Machine needs to be started using rive.play_state_machine(). Once it has been started it can be interacted with using go.set():
-- Start the State Machine named "State Machine 1"
rive.play_state_machine("#rivemodel", "State Machine 1")
-- Set the boolean value "Trigger 1" to true
go.set("#rivemodel", "Trigger 1", true)
-- Set the numeric value "Number 1" to 0.8
go.set("#rivemodel", "Number 1", 0.8)
-- Read the input value of the current State Machine
local v = rive.get_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1")
-- Read the input value of a nested artboard from the current State Machine
local v = rive.get_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1", "My_Nested_Artboard")
-- To go deeper into the nested hierarchy, you can add slashes between each scope
local v = rive.get_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1", "My_Nested_Artboard/My_Inner_Nested_Artboard")
-- Set the input value of the current State Machine
rive.set_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1", 0.5)
-- Set the input value of a nested artboard
rive.set_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1", 0.5, "My_Nested_Artboard")
-- Same as the example above, to go even deeper, separate the scopers with slashes!
rive.set_state_machine_input("#rivemodel", "Number 1", 0.5, "My_Nested_Artboard/My_Inner_Nested_Artboard")
Listeners
Listeners can be used to define click, hover, and mouse move actions that can change State Machine Inputs at runtime. You can forward mouse and touch actions to a State Machine in a Rive Model component like this:
function on_input(self, action_id, action)
if not action_id or action_id == hash("touch") then
if action.pressed then
rive.pointer_down("#rivemodel", action.x, action.y)
elseif action.released then
rive.pointer_up("#rivemodel", action.x, action.y)
else
rive.pointer_move("#rivemodel", action.x, action.y)
end
end
end
Events
Events that trigger while a State Machine is playing are sent to the callback function provided when calling rive.play_state_machine(url, state_machine_id, options, callback):
local function rive_event_handler(self, message_id, message)
print("received event", message.name)
pprint(message)
end
function init(self)
rive.play_state_machine("#rivemodel", "State Machine 1", nil, rive_event_handler)
end
If no callback is provided the events will be sent to the calling script as rive_event_trigger messages:
function init(self)
rive.play_state_machine("#rivemodel", "State Machine 1")
end
function on_message(self, message_id, message, sender)
if message_id == hash("rive_event_triggered") then
print("received event", message.name)
pprint(message)
end
end
Bone hierarchy
The individual bones in the Rive Scene skeleton are represented internally as game objects. In the Outline view of the Rive Scene the full hierarchy is visible.
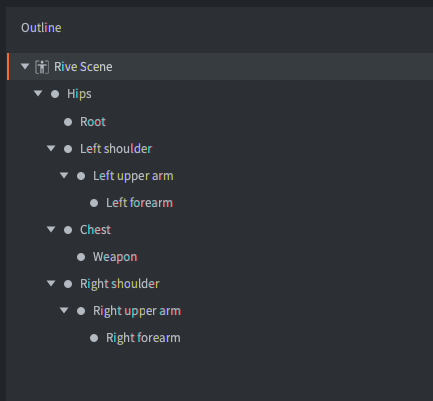
With the bone name at hand, it is possible to retrieve the instance id of the bone in runtime. The function rive.get_go() returns the id of the specified bone and it is, for instance, possible to child other game objects under the animated game object:
-- Attach pistol game object to the left forearm
local forearm = rive.get_go("#rivemodel", "Left forearm")
msg.post("pistol", "set_parent", { parent_id = forearm })
Getting and setting Text Runs
To set and get Text Runs, you can use the following functions:
local text = rive.get_text_run("#rivemodel", "my_text_run")
-- change the text to something else
rive.set_text_run("#rivemodel", "my_text_run", "Hello, World!")
-- you can also access text runs in nested artboards by passing in the artboard name:
rive.get_text_run("#rivemodel", "my_text_run", "my_nested_artboard")
-- accessing nested artboards within nested artboards is also possible
rive.get_text_run("#rivemodel", "my_text_run", "my_nested_artboard/my_other_nested_artboard")
-- the same works with set_text_run:
rive.set_text_run("#rivemodel", "my_text_run", "Hello, World!", "my_nested_artboard")
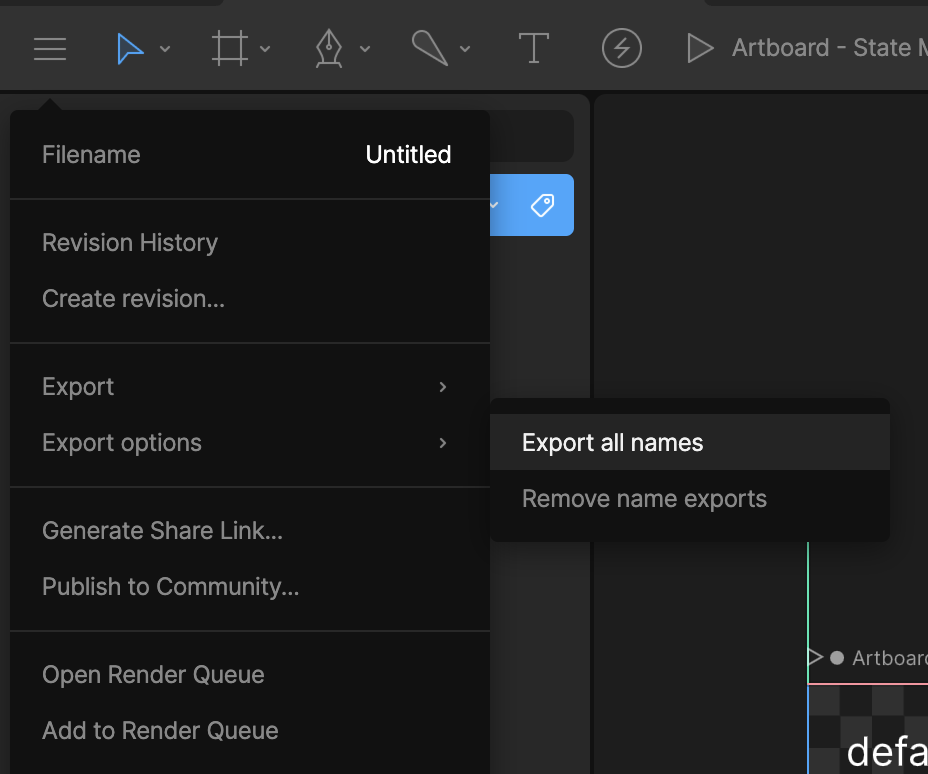
Note! You need to export all the names from within Rive to use these functions:
Source code
The source code is available on GitHub
API reference
- Rive animation
- Requirements
- Installation
- Windows
- Rendering
- Coordinate systems
- Mixing Defold and Rive content
- View matrix
- Blending
- Concepts
- Creating a Rive scene
- Creating Rive model components
- Rive model properties
- Runtime manipulation
- Playing animations
- Cursor animation
- Changing properties
- Interacting with State Machine Inputs
- Bone hierarchy
- Getting and setting Text Runs
- Source code
- English
- 中文 (Chinese)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Νεοελληνική γλώσσα (Greek)
- Italiano (Italian)
- Język polski (Polish)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Русский (Russian)
- Українська (Ukranian)
Did you spot an error or do you have a suggestion? Please let us know on GitHub!
GITHUB