Group and mask
The physics engine allows you to group your physics objects and filter how they should collide. This is handled by named collision groups. For each collision object you create two properties control how the object collides with other objects, Group and Mask.
For a collision between two objects to register both objects must mutually specify each other’s groups in their Mask field.
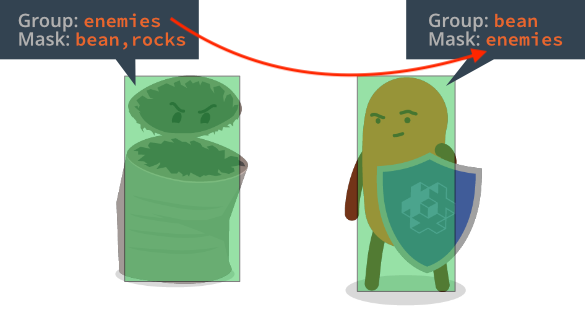
The Mask field can contain multiple group names, allowing for complex interaction scenarios.
Detecting collisions
When two collision objects with matching groups and masks collide the physics engine will generate collision messages that can be used in games to react to collisions.
- English
- 中文 (Chinese)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Νεοελληνική γλώσσα (Greek)
- Italiano (Italian)
- Język polski (Polish)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Русский (Russian)
- Українська (Ukranian)
Did you spot an error or do you have a suggestion? Please let us know on GitHub!
GITHUB