Project settings
The file game.project contains all project wide settings. It must stay in the root folder of the project and must be named game.project. The first thing the engine does when starting up and launching your game is look for this file.
Every setting in the file belongs to a category. When you open the file Defold presents all settings grouped by category.
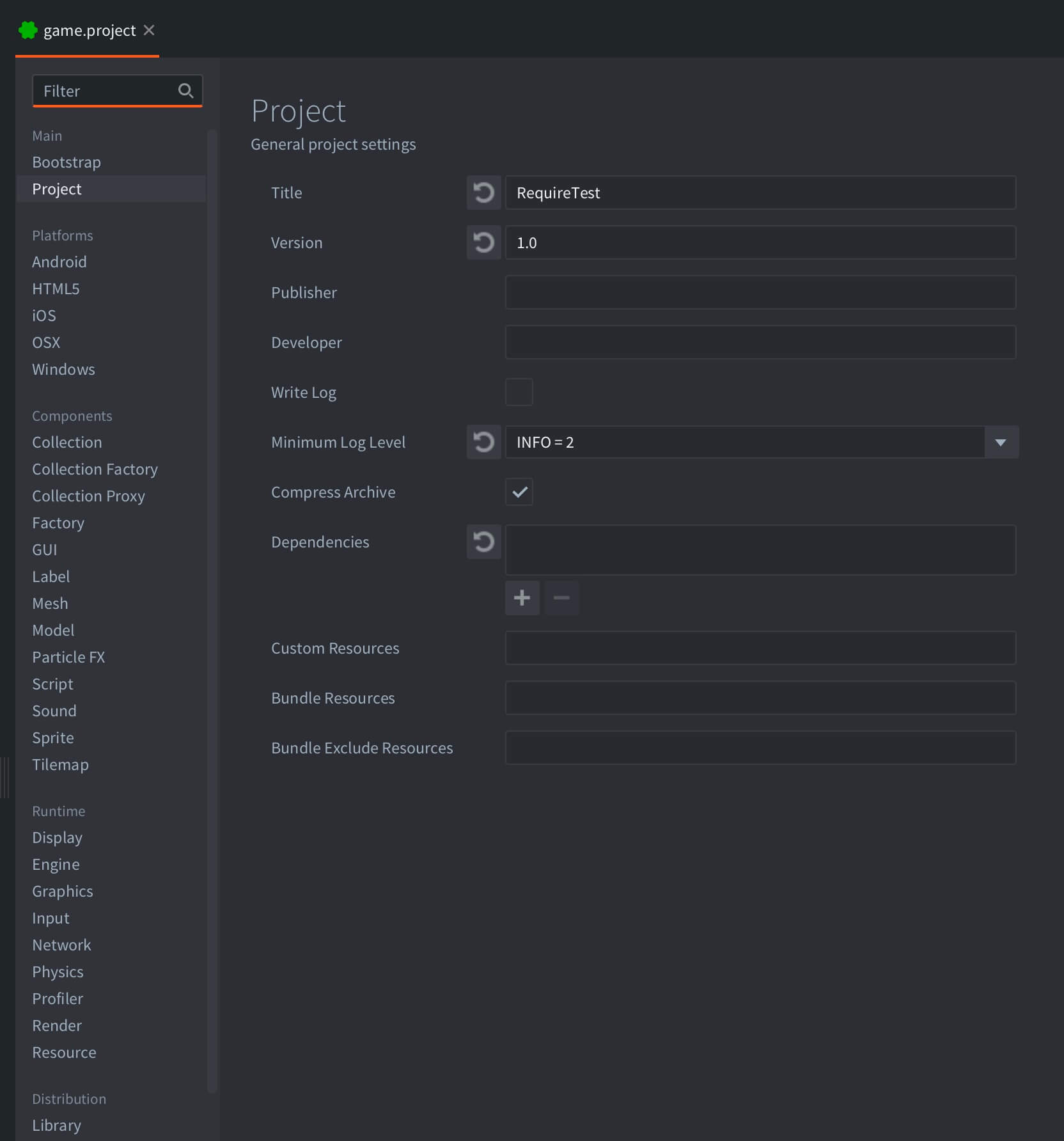
Below are all the available settings, arranged by section. Some settings are not yet exposed in the settings editor (these are marked “hidden setting” below), but can be set manually by right clicking game.project and selecting Open With ▸ Text Editor.
Sections and settings
Project
Title
The title of the application.
Version
The version of the application.
Write Log
When checked, the engine will write a log file log.txt in the project root. When running on iOS, the log file can be accessed through iTunes and the Apps tab and the File Sharing section. On Android, the file is stored in the app’s external storage. When running the dmengine development app, you can view the log with:
$ adb shell cat /mnt/sdcard/Android/data/com.defold.dmengine/files/log.txt
Compress Archive
Enables compression of archives when bundling. Note that this currently applies to all platforms except Android where the apk already contains all data compressed.
Dependencies
A list of URLs to the project Library URLs. Refer to the Libraries manual for more information.
Custom Resources
custom_resources
A comma separated list of resources that will be included in the project. If directories are specified, all files and directories in that directory are recursively included. The resources can be loaded using sys.load_resource(). Loading custom resources is covered in more detail in the File Access manual.
Bundle Resources
bundle_resources
A comma separated list of directories containing resource files and folders that should be copied as-is into the resulting package when bundling. The directories must be specified with an absolute path from the project root, for example /res. The resource directory must contain subfolders named by platform, or architecture-platform.
Supported platforms are ios, android, osx, win32, linux, web, switch
A subfolder named common is also allowed, containing resource files common for all platforms.
Access to files within the the bundle resources is platform specific. The Lua module io is one way to do it. Care must be taken to have the correct file paths for the platform.
(e.g. prefix using “file:///android_asset/” on Android). Loading files is covered in more detail in the File Access manual.
Bundle Exclude Resources
bundle_exclude_resources
A comma separated list of resources that should not be included in the bundle.
That is, they’re removed from the result of the collection of the bundle_resources step.
Bootstrap
Main Collection
File reference of the collection to use for starting the application, /logic/main.collection by default.
Render
Which render setup file to use, which defines the render pipeline, /builtins/render/default.render by default.
Library
Include Dirs
A space separated list of directories that should be shared from your project via library sharing. Refer to the Libraries manual for more information.
Script
Shared State
Check to share a single Lua state between all script types, unchecked by default.
Engine
Run While Iconified
Allow the engine to continue running while the application window is iconified (desktop platforms only), false by default.
Fixed Update Frequency
The update frequency of the fixed_update(self, dt) lifecycle function. In Hertz. 60 by default.
Display
Width
The width in pixels of the application window, 960 by default.
Height
The height in pixels of the application window, 640 by default.
High Dpi
Creates a high dpi back buffer on displays that support it. Typically the game will render in double the resolution than what is set in the Width and Height settings, which will still be the logical resolution used in scripts and properties.
Samples
How many samples to use for super sampling anti-aliasing. It sets the GLFW_FSAA_SAMPLES window hint. It is 0 by default, which means that anti-aliasing is turned off.
Fullscreen
Check if the application should start full screen. If unchecked, the application runs windowed.
Update Frequency
The desired frame rate in Hertz. Set to 0 for variable frame rate. A value larger than 0 will result in a fixed frame rate capped at runtime towards the actual frame rate (which means that you cannot update the game loop twice in an engine frame). Use sys.set_update_frequency(hz) to change this value at runtime.
Swap interval
An integer setting that sets the OpenGL swap interval. Does not work with Vulkan. 0 disables vsync. Default is 1.
Display Profiles
Specifies which display profiles file to use, /builtins/render/default.display_profilesc by default. Learn more in the GUI Layouts manual.
Dynamic Orientation
Check if the app should dynamically switch between portrait and landscape on device rotation. Note that the development app does not currently respect this setting.
Render
Clear Color Red
Clear color red channel, used by the render script and when the window is created.
Clear Color Green
Clear color green channel, used by the render script and when the window is created.
Clear Color Blue
Clear color blue channel, used by the render script and when the window is created.
Clear Color Alpha
Clear color alpha channel, used by the render script and when the window is created.
Physics
Type
Which type of physics to use, 2D (default) or 3D.
Gravity Y
World gravity along y-axis, -10 by default (natural gravity)
Debug
Check if physics should be visualized for debugging.
Debug Alpha
Alpha component value for visualized physics, 0–1. The value is 0.9 by default.
World Count
Max number of concurrent physics worlds, 4 by default. If you load more than 4 worlds simultaneously through collection proxies you need to increase this value. Be aware that each physics world allocates a fair amount of memory.
Gravity X
World gravity along x-axis, 0 by default.
Gravity Z
World gravity along z-axis, 0 by default.
Scale
Tells the physics engine how to scale the physics worlds in relation to the game world for numerical precision, 0.01–1.0. If the value is set to 0.02, it means that the physics engine will view 50 units as 1 meter ($1 / 0.02$). The default value is 1.0.
Allow Dynamic Transforms
Check if the physics engine should apply the transform of a game object to any attached collision object components. This can be used to move, scale and rotate collision shapes, even those that are dynamic. true by default.
Use Fixed Timestep
Check if the physics engine should use fixed and framerate independent updates. Use this setting in combination with the fixed_update(self, dt) lifecycle function and the engine.fixed_update_frequency project setting to interact with the physics engine at regular intervals. For new projects the recommended setting is true. false by default
Debug Scale
How big to draw unit objects in physics, like triads and normals, 30 by default.
Max Collisions
How many collisions that will be reported back to the scripts, 64 by default.
Max Contacts
How many contact points that will be reported back to the scripts, 128 by default.
Contact Impulse Limit
Ignore contact impulses with values less than this setting, 0.0 by default.
Ray Cast Limit 2d
The max number of 2d ray cast requests per frame. 64 by default.
Ray Cast Limit 3d
The max number of 3d ray cast requests per frame. 128 by default.
Trigger Overlap Capacity
The maximum number of overlapping physics triggers. 16 by default.
Graphics
Default Texture Min Filter
Specifies which filtering to use for minification filtering, linear by default.
Default Texture Mag Filter
Specifies which filtering to use for magnification filtering, linear by default.
Max Draw Calls
The max number of render calls, 1024 by default.
Max Characters:
The number of characters pre-allocated in the text rendering buffer, i.e. the number of characters that can be displayed each frame, 8192 by default.
Max Debug Vertices
The maximum number of debug vertices. Used for physics shape rendering among other things, 10000 by default.
Texture Profiles
The texture profiles file to use for this project, /builtins/graphics/default.texture_profiles by default.
Verify Graphics Calls
Verify the return value after each graphics call and report any errors in the log.
Shader
Output SPIR-V
Compile and output SPIR-V shaders for use with Metal or Vulkan.
Input
Repeat Delay
Seconds to wait before a held down input should start repeating itself, 0.5 by default.
Repeat Interval
Seconds to wait between each repetition of a held down input, 0.2 by default.
Gamepads
File reference of the gamepads config file, which maps gamepad signals to OS, /builtins/input/default.gamepads by default.
Game Binding
File reference of the input config file, which maps hardware inputs to actions, /input/game.input_binding by default.
Use Accelerometer
Check to make the engine receive accelerator input events each frame. Disabling accelerometer input may give some performance benefit, checked by default.
Resource
Http Cache
If checked, a HTTP cache is enabled for faster loading of resources over the network to the running engine on device, unset by default.
Uri
Where to find the project build data, in URI format.
Max Resources
The max number of resources that can be loaded at the same time, 1024 by default.
Network
Http Timeout
The HTTP timeout in seconds. Set to 0 to disable timeout, which is the default.
Http Thread Count
The number of worker threads for the HTTP service.
Http Cache Enabled
Check to enable the HTTP cache for network requests (using http.request(). The HTTP cache will store the response associated with a request and reuse the stored response for subsequent requests. The HTTP cache supports the ETag and Cache-Control: max-age HTTP response headers.
SSL Certificates
File containing SSL root certificates to use when verifying the certificate chain during SSL handshakes.
Collection
Max Instances
Max number of game object instances in a collection, 1024 by default.
Max Input Stack Entries
Max number of game objects in the input stack, 16 by default.
Sound
Gain
Global gain (volume), 0–1, The value is 1 by default.
Max Sound Data
Max number of sound resources, i.e the number of unique sound files at runtime, 128 by default.
Max Sound Buffers
(Currently not used) Max number of concurrent sound buffers, 32 by default.
Max Sound Sources
(Currently not used) Max number of concurrently playing sounds, 16 by default.
Max Sound Instances
Max number of concurrent sound instances, i.e. actual sounds played at the same time. 256 by default.
Use Thread
If checked, the sound system will use threads for sound playback to reduce risk of stutter when the main thread is under heavy load. Checked by default.
Sprite
Max Count
Max number of sprites per collection, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Subpixels
Check to allow sprites to appear unaligned with respect to pixels, checked by default.
Tilemap
Max Count
Max number of tile maps per collection, 16 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Max Tile Count
Max number of concurrent visible tiles per collection, 2048 by default.
Spine
Max Count
Max number of spine model components, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Mesh
Max Count
Max number of mesh components per collection, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Model
Max Count
Max number of model components per collection, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
GUI
Max Count
Max number of GUI components, 64 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Max Particlefx Count
The max number of concurrent emitters, 64 by default.
Max Particle Count
The max number of concurrent particles, 1024 by default.
Max Animation Count
The max number of active animations in gui, 1024 by default.
Label
Max Count
Max number of labels, 64 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Subpixels
Check to allow labels to appear unaligned with respect to pixels, checked by default.
Particle FX
Max Count
The max number of concurrent emitters, 64 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Max Particle Count
The max number of concurrent particles, 1024 by default.
Collection proxy
Max Count
Max number of collection proxies, 8 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Collection factory
Max Count
Max number of collection factories, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
Factory
Max Count
Max number of game object factories, 128 by default. (See information about component max count optimizations).
iOS
App Icon 57x57–180x180
Image file (.png) to use as application icon at given width and height dimensions W × H.
Launch Screen
Storyboard file (.storyboard). Learn more about how to create one in the iOS manual.
Pre Rendered Icons
(iOS 6 and earlier) Check if your icons are pre-rendered. If this is unchecked the icons will get a glossy highlight added automatically.
Bundle Identifier
The bundle identifier lets iOS recognize any updates to your app. Your bundle ID must be registered with Apple and be unique to your app. You cannot use the same identifier for both iOS and macOS apps. Must consist of two or more segments separated by a dot. Each segment must start with a letter. Each segment must only consist of alphanumeric letters, the underscore or hypen (-) character (see CFBundleIdentifier)
Bundle Name
The bundle short name (15 characters) (see CFBundleName).
Bundle Version
The bundle version, either a number or x.y.z. (see CFBundleVersion)
Info.plist
If specified, use this info.plist file when bundling your app.
Privacy Manifest
The Apple Privacy Manifest for the application. The field will default to /builtins/manifests/ios/PrivacyInfo.xcprivacy.
Custom Entitlements
If specified, the entitlements in the supplied provisioning profile (.entitlements, .xcent, .plist) will be merged with the entitlements from the provisioning profile supplied when bundling the application.
Override Entitlements
If checked the Custom Entitlements will replace the ones in the provisioning profile when bundling. Must be used in combination with the Custom Entitlements setting above.
Default Language
The language used if the application doesn’t have user’s preferred language in Localizations list (see CFBundleDevelopmentRegion). Use the two-letter ISO 639-1 standard if preferred language is available there or the three-letter ISO 639-2.
Localizations
This field contains comma-separated strings identifying the language name or ISO language designator of the supported localizations (see CFBundleLocalizations).
Android
App Icon 36x36–192x192
Image file (.png) to use as application icon at given width and height dimensions W × H.
Push Icon Small–LargeXxxhdpi
Image files (.png) to be used as custom push notification icon on Android. The icons will automatically be used for both local or remote push notifications. If not set the application icon will be used by default.
Push Field Title
Specifies which payload JSON field should be used as notification title. Leaving this setting empty makes the pushes default to the application name as title.
Push Field Text
Specifies which payload JSON field should be used as notification text. If left empty, the text in the field alert is used, just as on iOS.
Version Code
An integer value indicating the version of the app. Increase the value for each subsequent update.
Package
Package identifier. Must consist of two or more segments separated by a dot. Each segment must start with a letter. Each segment must only consist of alphanumeric letters or the underscore character.
Gcm Sender Id
Google Cloud Messaging Sender Id. Set this to the string assigned by Google to enable push notifications.
Manifest
If set, use the specified Android manifest XML file when bundling.
Iap Provider
Specifies which store to use. Valid options are Amazon and GooglePlay, GooglePlay by default.
Input Method
Specifies which method to use to get keyboard input on Android devices. Valid options are KeyEvent (old method) and HiddenInputField (new). KeyEvent by default.
Immersive Mode
If set, hides the navigation and status bars and lets your app capture all touch events on the screen.
Debuggable
Whether or not the application can be debugged using tools such as GAPID or Android Studio. This will set the android:debuggable flag in the Android manifest (official documentation).
Extract Native Libs
Specifies whether the package installer extracts native libraries from the APK to the file system. If set to false, your native libraries are stored uncompressed in the APK. Although your APK might be larger, your application loads faster because the libraries load directly from the APK at runtime. This will set the android:extractNativeLibs flag in the Android Manifest (official documentation). true by default.
macOS
App Icon
Image file (.png) to use as application icon on macOS.
Info.plist
If set, use the specified info.plist file when bundling.
Privacy Manifest
The Apple Privacy Manifest for the application. The field will default to /builtins/manifests/osx/PrivacyInfo.xcprivacy.
Bundle Identifier
The bundle identifier lets macOS recognize updates to your app. Your bundle ID must be registered with Apple and be unique to your app. You cannot use the same identifier for both iOS and macOS apps. Must consist of two or more segments separated by a dot. Each segment must start with a letter. Each segment must only consist of alphanumeric letters, the underscore or hypen (-) character.
Default Language
The language used if the application doesn’t have user’s preferred language in Localizations list (see CFBundleDevelopmentRegion). Use the two-letter ISO 639-1 standard if preferred language is available there or the three-letter ISO 639-2.
Localizations
This field contains comma-separated strings identifying the language name or ISO language designator of the supported localizations (see CFBundleLocalizations).
Windows
App Icon
Image file (.ico) to use as application icon on Windows. Read more about how to create a .ico file in the Windows manual.
Iap Provider
Specifies which store to use. Valid options are None and Gameroom, None by default.
HTML5
Heap Size
Heap size (number of megabytes) for Emscripten to use. By default this value is 256MB.
.html Shell
Use the specified template HTML file when bundling. By default /builtins/manifests/web/engine_template.html.
Custom .css
Use the specified theme CSS file when bundling. By default /builtins/manifests/web/light_theme.css.
Splash Image
If set, use the specified splash image on startup when bundling instead of Defold logo.
Archive Location Prefix
When bundling for HTML5 game data is split up into one or more archive data files. When the engine starts the game, these archive files are read into memory. Use this setting to specify the location of the data, archive by default.
Archive Location Suffix
Suffix to be appended to the archive files. Useful to, for instance, force non-cached content from a CDN (?version2 for example).
Engine Arguments
List of arguments that will be passed to the engine.
Show Fullscreen Button
Enables Fullscreen Button in index.html file. By default true.
Show Made With Defold
Enables Made With Defold link in index.html file. By default true.
Scale Mode
Specifies which method to use to scale the game canvas. By default Downscale Fit.
IAP
Auto Finish Transactions
Check to automatically finish IAP transactions. If unchecked, you need to explicitly call iap.finish() after a successful transaction, checked by default.
Live update
Private Key
If set, use the specified private key file when bundling live update content. If no key file is set, a key is generated.
Public Key
If set, use the specified public key file when bundling live update content. If no key file is set, a key is generated.
Native extension
App Manifest
If set, use the app manifest to customize the engine build. This allows you to remove unused parts from the engine to decrease the final binary size. Learn how to exclude unused feature in the application manifest manual.
Profiler
Track Cpu
If checked, enable CPU profiling in release versions of the builds. Normally, you can only access profiling information in debug builds.
File format
The format of the settings file is simple text (INI format) and can be edited by any standard text editor. The format looks like this:
[category1]
setting1 = value
setting2 = value
[category2]
...
A real example is:
[bootstrap]
main_collection = /main/main.collectionc
which means that the setting main_collection belongs to the bootstrap category. Whenever a file reference is used, like the example above, the path needs to be appended with a ‘c’ character, which means you’re referencing the compiled version of the file. Also note that the folder containing game.project will be the project root, which is why there is an initial ‘/’ in the setting path.
Setting config values on engine startup
When the engine starts, it is possible to provide config values from the command line that override the game.project settings:
# Specify a bootstrap collection
$ dmengine --config=bootstrap.main_collection=/my.collectionc
# Set two custom config values
$ dmengine --config=test.my_value=4711 --config=test2.my_value2=1234
Custom values can—just like any other config value—be read with sys.get_config():
local my_value = tonumber(sys.get_config("test.my_value"))
Component max count optimizations
The game.project settings file contains many values specifying the maximum number of a certain resource that can exist at the same time, often counted per loaded collection (also called world). The Defold engine will use these max values to preallocate memory for this amount of memory to avoid dynamic allocations and memory fragmentation while the game is running.
The Defold data structures used to represent components and other resources are optimized to use as little memory as possible but care should still be taken when setting the values to avoid allocating more memory than is actually necessary.
To further optimize memory usage the Defold build process will analyse the content of the game and override the max counts if it is possible to know for certain the exact amount:
- If a collection doesn’t contain any factory components the exact amount of each component will be allocated and the max count values will be ignored.
- If a collection contains a factory component the spawned objects will be analysed and the max count will be used for components that can be spawned from the factories.
- If a collection contains a factory or a collection factory with activated “Dynamic Prototype” option, this collection will use the max counters.
Custom project settings
It is possible to define custom settings for the main project or for a native extension. Custom settings for the main project must be defined in a game.properties file in the root of the project. For a native extension they should be defined in an ext.properties file next to the ext.manifest file.
The settings file uses the same INI format as game.project and property attributes are defined using a dot notation with a suffix:
[my_category]
my_property.private = 1
...
The default meta file that is always applied is available here
The following attributes are currently available:
// `type` - used for the value string parsing (only in bob.jar for now)
my_property.type = string // one of the following values: bool, string, number, integer, string_array, resource
// `help` - used as help tip in the editor (not used for now)
my_property.help = string
// `default` - value used as default if user didn't set value manually (only in bob.jar for now)
my_property.default = string
// `private` - private value used during the bundle process but will be removed from the bundle itself
my_property.private = 1 // boolean value 1 or 0
At the moment meta properties are used only in bob.jar when bundling application, but later will be parsed by the editor and represented in the game.project viewer.
- English
- 中文 (Chinese)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Νεοελληνική γλώσσα (Greek)
- Italiano (Italian)
- Język polski (Polish)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Русский (Russian)
- Українська (Ukranian)
Did you spot an error or do you have a suggestion? Please let us know on GitHub!
GITHUB