Hinge joint physics
Setup
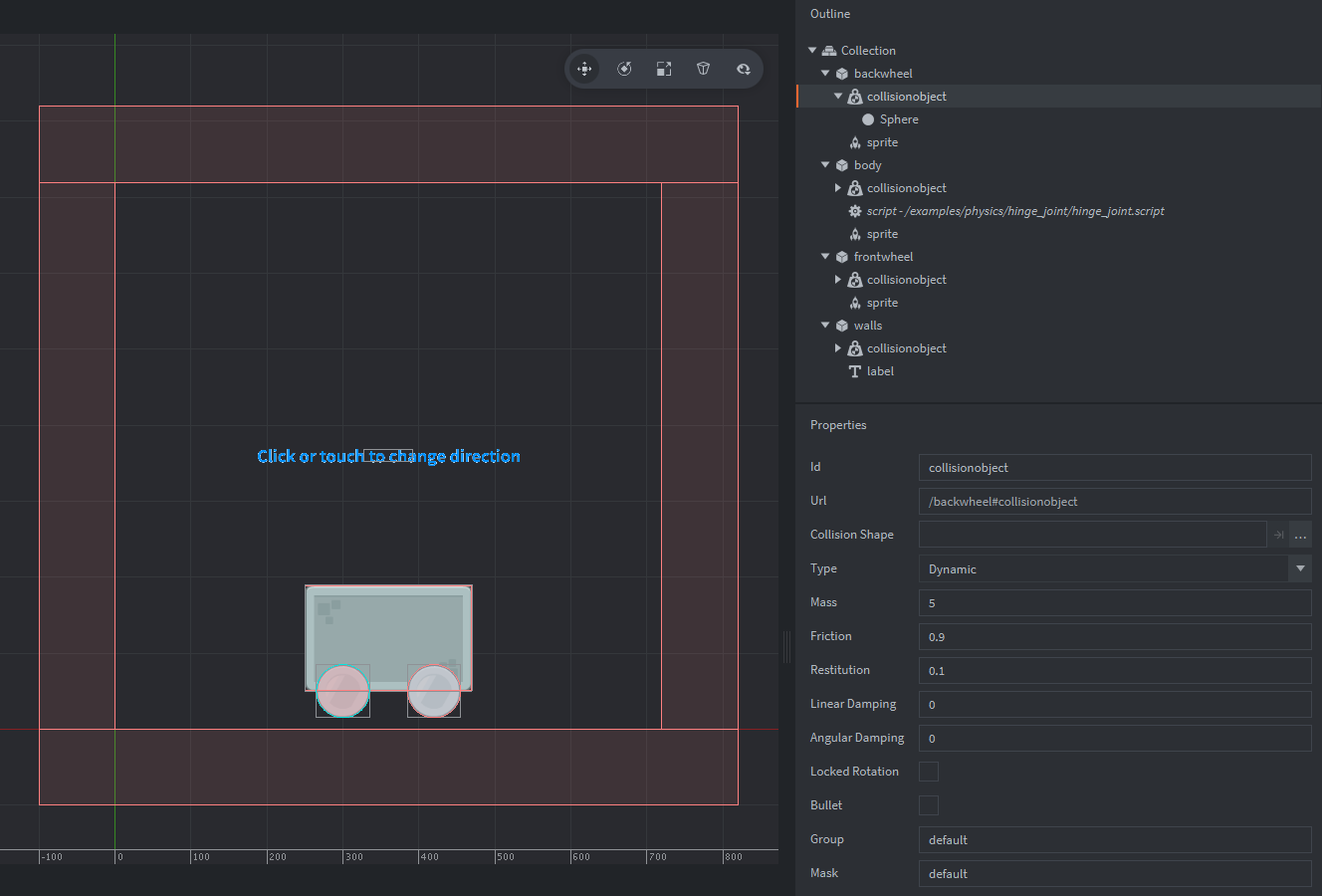
The setup consists of four game objects. The game.project physics GravityY property is set to -500 to match the scale of the setup.
- body
- The square stone block. Contains:
- A Sprite component with the stone block image.
- A Collision object component. The Type is set to
DYNAMIC. A box Shape matching the sprite image is added to the components. - A script that joines the wheel game objects to to the body and reacts to user input by changing the direction of the rotation of the hinge joints.
- A label with an instruction to the user.
- frontwheel
- The cirular metal wheel. Contains:
- A Sprite component with the metal circle image.
- A Collision object component. Also has Type set to
DYNAMIC, Friction set to 0.9 and Restitution to 0.1. A box Shape matching the sprite image is added to the components.
- backwheel
- The same as above.
- walls
- The outer walls. Contains:
- A Collision object component. The Type is set to
STATIC. 4 box Shapes are added to the component. These are placed just outside of the game view.
- A Collision object component. The Type is set to
Scripts
hinge_joint.script
local frontwheel = "frontwheel#collisionobject" -- <1>
local backwheel = "backwheel#collisionobject"
local body = "body#collisionobject"
local center_anchor = vmath.vector3(0, 0, 0)
local frontwheel_anchor = vmath.vector3(60, -60, 0)
local backwheel_anchor = vmath.vector3(-60, -60, 0)
local hinge_props = { enable_motor = true, enable_limit = false, max_motor_torque = 3000, motor_speed = 1 * 2 * math.pi}
function init(self)
msg.post(".", "acquire_input_focus") -- <2>
self.forward = true -- <3>
physics.create_joint(physics.JOINT_TYPE_HINGE, frontwheel, "frontwheel", center_anchor, body, frontwheel_anchor, hinge_props) -- <4>
physics.create_joint(physics.JOINT_TYPE_HINGE, backwheel, "backwheel", center_anchor, body, backwheel_anchor, hinge_props)
end
function on_input(self, action_id, action)
if action_id == hash("touch") and action.pressed then -- <5>
self.forward = not self.forward -- <6>
if self.forward then -- <7>
hinge_props.motor_speed = 5 * 2 * math.pi -- <8>
else -- <9>
hinge_props.motor_speed = -5 * 2 * math.pi -- <10>
end
physics.set_joint_properties(frontwheel, "frontwheel", hinge_props) -- <11>
physics.set_joint_properties(backwheel, "backwheel", hinge_props)
end
end
--[[
1. Store collision objects ids, vectors used for anchors and hinge properties used for creating joints in local variables.
2. Tell the engine that this object ("." is shorthand for the current game object) should listen to input. Any input will be received in the `on_input()` function.
3. Set a flag self.forward used to define the direction of the rotation of the joined wheels.
4. Create a joint of type "hinge" (a revolute joint, a pin or an axle) between a center of frontwheel collision object and an anchor ((-60,-60) from the center) on body collision object with provided properties. Do the same for the second wheel.
5. If we receive input (touch or mouse click) we switch the direction of rotation of the wheels.
6. Negate the current flag defining the direction.
7. If the direction flag is true, we are going forward.
8. Set the motor_speed property to 5 revolutions per second in clockwise direction.
9. If the direction flag is false, we are going backward.
10. Set the motor_speed property to 5 revolutions per second in counter-clockwise direction.
11. Set the new properties with changed speed for the joints.
--]]