Panning
Setup
Overview : A coin bounces around the screen and on collision detection we get the coins x position then normalize that value for use in the sound components pan property. As the API states “The pan on the sound-component. The valid range is from -1.0 to 1.0, representing -45 degrees left, to +45 degrees right.” we can use this information along with our x value from our coin object and normalize it into the correct range.
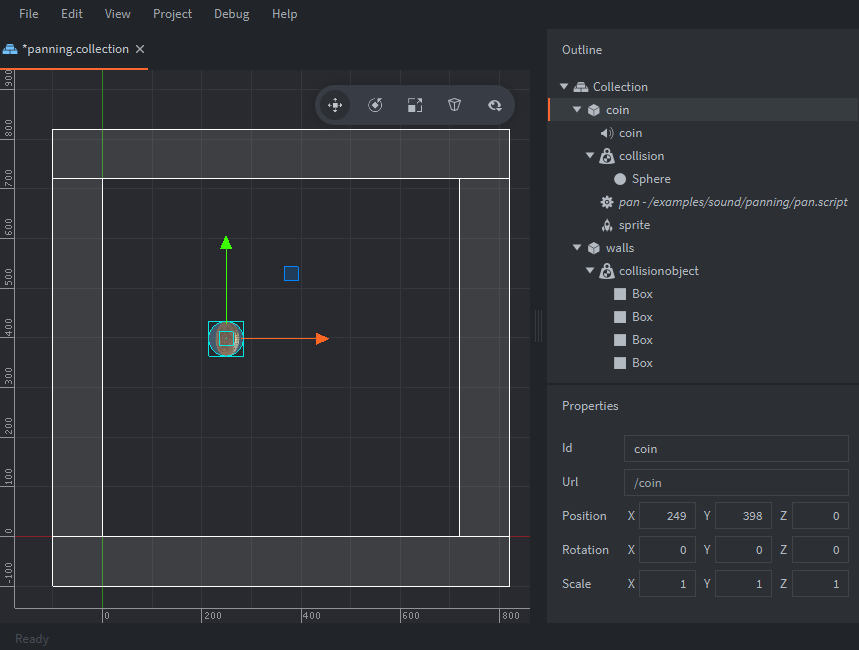
The setup consists of a coin game object, three stone objects and walls for collision.
- Coin
- contains:
- A Sound component.
- A Collision component. With Type set to
DYNAMICand a Sphere Shape. - A script used to set initial coin movement then set pan value and play a sound on collision.
- A sprite component with default animation set as coin
- Stones
- contains:
- A Collision component set to
STATICand 1 box Shape to match the sprite image.
- A Collision component set to
- Walls
- contains:
- A Collision component set to
STATICand 4 box Shapes that make up the walls along the bounds of the game screen.
- A Collision component set to
Scripts
pan.script
local position_min = 0 -- <1>
local position_max = sys.get_config_int("display.width") -- <2>
local function normalize_position(x_position) -- <3>
local average = (position_min + position_max) / 2
local range = (position_max - position_min) / 1.8
local result = (x_position - average) / range
return result
end
function on_message(self, message_id, message, sender) -- <4>
if message_id == hash("collision_response") then
local coin_pos = normalize_position(go.get_position().x)
sound.play("#coin", { gain = 0.6, pan = coin_pos } )
end
end
--[[
1. - Local variable to represent the minimum x position value.
2. - Local variable to represent the maximum x position value. sys.get_config_int("display.width") to get
screen width used for maximum x position value.
3. - This function uses the screen x position min & max local variables that is set at the top
of the script to get an average and range then pass in the coin objects x position into
result to get a normalized value and the function returns that value. note: in range if we
divide by 2.0 we would get range -1.0 to 1.0 full 45 degree pan at min/max positions, instead
use 1.8 to get around a 40 deg pan that way we always get a little bit of sound in both
left and right channel outputs no matter the min/max position.
4. - When a collision_response is received we pass in the coin objects x position into the
normalize_position function and set the results to the local variable coin_pos. Then play
a sound and pass in coin_pos into the sounds pan property.
Now we have simple sound localization using the pan property. If you close your eyes, you should
be able to gauge which direction the collisions are occurring.(as long as you are using stereo sound)
--]]