Fixed timestep interpolation
Setup
This example demonstrates two rendering paths while physics runs at a fixed frequency:
Not interpolated: visual sprite follows the dynamic body directly (visually looks like it has a stepped motion).Interpolated: visual sprite is interpolated between fixed physics states (smooth motion).
The key idea is to separate physics simulation from rendering:
- Keep the transforms of the game objects with dynamic collision objects as the source of truth.
- Set position of the visual representation based on the position of the physics objects.
- Interpolate only the visual representation transform.
Setup
In game.project:
- In the
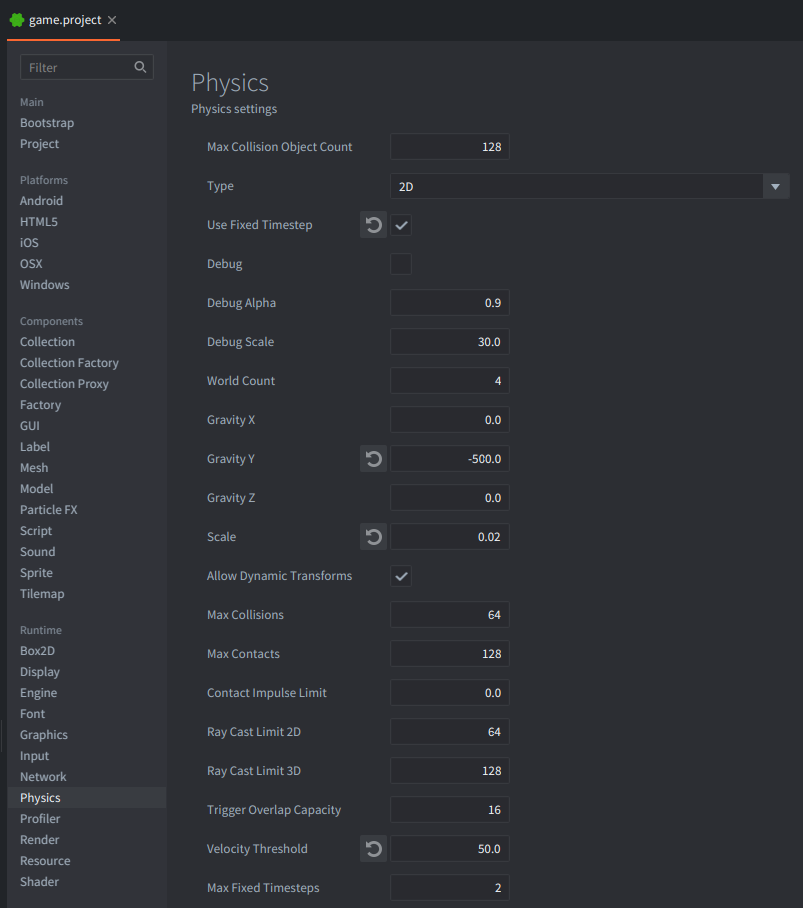
Physicssection setUse_Fixed_Timestepenabled andVelocity Thresholdto 50 (It is necessary for 2D physics, because velocity threshold is scaled with the scale option, and in the end it should be 1.0 internally in Box2D, so if Scale is set to 0.02, the velocity threshold should be 50 = 1.0 / 0.02). Gravity is set arbitraly for this example to -500.
- In the
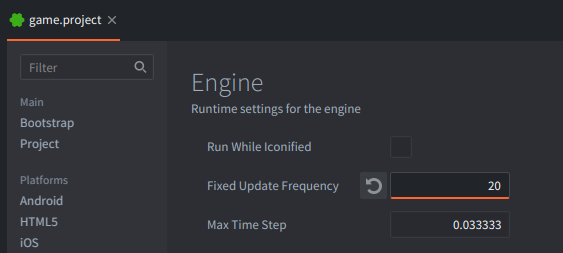
Enginesection setFixed Update Frequencyto a low value, e.g. 20, so the difference is easy to see.
The setup consists of 5 game objects:
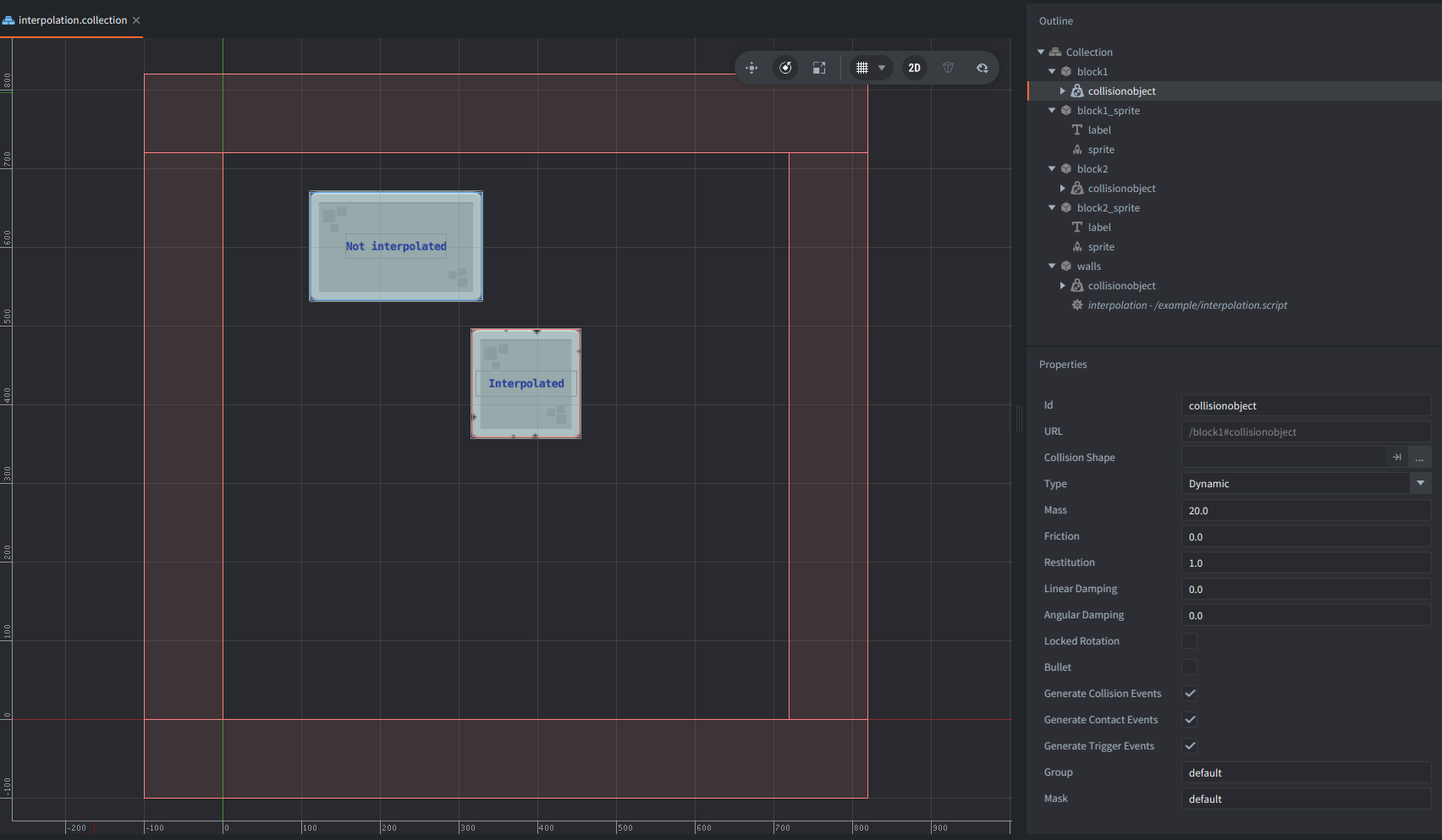
walls- Static borders and the script host.
- A static Collision object component.
- A script component using
/example/interpolation.script.
block1- Game Object for the non-interpolated path for the physics component.
- A dynamic Collision object component.
- No sprite (physics-only object).
block1_sprite- Game Object for the non-interpolated path for the visual representation.
- A Sprite component.
- A Label component (with text
Not interpolated).
block2- Game Object for the interpolated path for the physics component.
- A dynamic Collision object component.
- No sprite (physics-only object).
block2_sprite- Game Object for the non-interpolated path for the visual representation.
- A Sprite component.
- A Label component (with text
Interpolated).
Script Behavior
/example/interpolation.script:
- Keeps a two-sample fixed-state buffer for
block2:previous= previous fixed physics samplecurrent= current fixed physics sample
- In
fixed_update(), shifts values (currentdata becomespreviousdata) and samples a newcurrenttransform from the objects controlled by the dynamic collision objects. - In
update(), computes render progress inside the current fixed interval:alpha = render_accumulator / fixed_dt
- Renders:
block1_spritefrom rawblock1transform.block2_spritefrom interpolated transform (position is interpolated usingvmath.lerp(), and rotation is interpolated usingvmath.slerp()).
Expected Result
At runtime:
block1_spriteappears updated at the fixed frequency.block2_spriteappears updated each frame.
Scripts
interpolation.script
-- This example compares two render paths when physics runs in fixed timestep mode:
-- 1) not_interpolated_block: visual representation copies physics representation transform directly
local not_interpolated_block = {
physics_go = "/block1",
sprite_go = "/block1_sprite",
}
-- 2) interpolated_block: visual representation is interpolated between previous and current fixed states
local interpolated_block = {
physics_go = "/block2",
sprite_go = "/block2_sprite",
}
-- Store fixed update interval in seconds from game.project Fixed Update Frequency.
local fixed_dt = 1 / (sys.get_config_number("engine.fixed_update_frequency") or 20)
function init(self)
-- Render-time remainder inside the current fixed-step interval.
self.render_accumulator = 0
-- Two-sample buffer for interpolation:
-- previous_* = transform from previous fixed update
-- current_* = transform from current fixed update
-- Initialize both from real physics representation state.
self.previous_fixed_position = go.get_position(interpolated_block.physics_go)
self.current_fixed_position = self.previous_fixed_position
self.previous_fixed_rotation = go.get_rotation(interpolated_block.physics_go)
self.current_fixed_rotation = self.previous_fixed_rotation
end
function fixed_update(self, dt)
-- Shift the transform data from current state to previous state
-- and sample new fixed state from the game object with the dynamic collision object component.
self.previous_fixed_position = self.current_fixed_position
self.previous_fixed_rotation = self.current_fixed_rotation
self.current_fixed_position = go.get_position(interpolated_block.physics_go)
self.current_fixed_rotation = go.get_rotation(interpolated_block.physics_go)
end
function update(self, dt)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- For not interpolated object:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Copy physics transform directly to the visual representation.
local not_interpolated_position = go.get_position(not_interpolated_block.physics_go)
local not_interpolated_rotation = go.get_rotation(not_interpolated_block.physics_go)
go.set_position(not_interpolated_position, not_interpolated_block.sprite_go)
go.set_rotation(not_interpolated_rotation, not_interpolated_block.sprite_go)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- For interpolated object:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Keep accumulator inside [0, fixed_dt) using modulo wrap.
self.render_accumulator = math.fmod(self.render_accumulator + dt, fixed_dt)
-- Base alpha from render progress between fixed samples:
-- alpha=0 -> previous sample, alpha=1 -> current sample.
local alpha = self.render_accumulator / fixed_dt
-- Calculate the difference between the current and previous fixed positions.
local position_difference = self.current_fixed_position - self.previous_fixed_position
-- Position interpolation is linear (lerp).
local interpolated_position = self.previous_fixed_position + position_difference * alpha
-- Rotation interpolation is spherical (slerp).
local interpolated_rotation = vmath.slerp(alpha, self.previous_fixed_rotation, self.current_fixed_rotation)
-- Render blended transform.
go.set_position(interpolated_position, interpolated_block.sprite_go)
go.set_rotation(interpolated_rotation, interpolated_block.sprite_go)
end