This translation is community contributed and may not be up to date. We only maintain the English version of the documentation. Read this manual in English
脚本属性
脚本属性提供了一种简单而强大的方式,用于定义和暴露特定游戏对象实例的自定义属性。脚本属性可以在编辑器中直接在特定实例上编辑,并且它们的设置可以在代码中使用,以改变游戏对象的行为。在许多情况下,脚本属性非常有用:
- 当您想在编辑器中为特定实例覆盖值,从而提高脚本的可重用性时。
- 当您想用初始值生成游戏对象时。
- 当您想为属性的值创建动画时。
- 当您想从一个脚本访问另一个脚本中的状态数据时。(请注意,如果您在对象之间频繁访问属性,最好将数据移动到共享存储中。)
常见的用例是设置特定敌人AI的生命值或速度、拾取对象的色调颜色、精灵的图集,或者按钮对象在被按下时应该发送什么消息—以及/或者发送到哪里。
定义脚本属性
脚本属性是通过使用go.property()特殊函数将它们添加到脚本组件中的。该函数必须在顶层使用—在任何生命周期函数(如init()和update())之外。为属性提供的默认值决定了属性的类型:number、boolean、hash、msg.url、vmath.vector3、vmath.vector4、vmath.quaternion和resource(见下文)。
请注意,哈希值的反转仅在Debug构建中有效,以方便调试。在Release构建中,反转的字符串值不存在,因此对hash值使用tostring()来从中提取字符串是没有意义的。
-- can.script
-- 为生命值和攻击目标定义脚本属性
go.property("health", 100)
go.property("target", msg.url())
function init(self)
-- 存储目标的初始位置。
-- self.target 是引用另一个对象的url。
self.target_pos = go.get_position(self.target)
...
end
function on_message(self, message_id, message, sender)
if message_id == hash("take_damage") then
-- 减少生命值属性
self.health = self.health - message.damage
if self.health <= 0 then
go.delete()
end
end
end
然后,任何由此脚本创建的脚本组件实例都可以设置属性值。
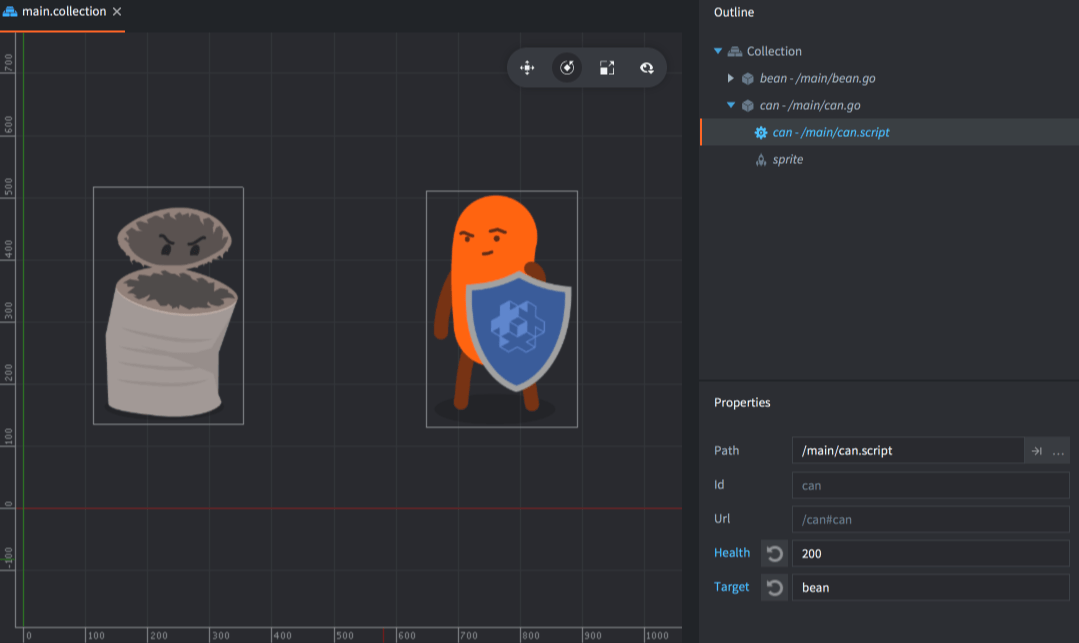
在编辑器中的Outline视图中选择脚本组件,属性会出现在Properties视图中,允许您编辑它们:
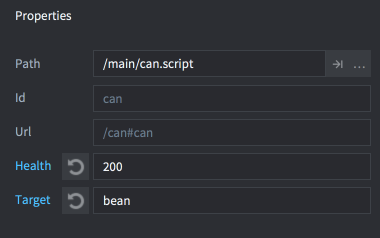
任何被新的实例特定值覆盖的属性都会标记为蓝色。单击属性名称旁边的重置按钮可以将值恢复为默认值(在脚本中设置)。
脚本属性在构建项目时被解析。值表达式不会被计算。这意味着像go.property("hp", 3+6)这样的东西不会工作,而go.property("hp", 9)会工作。
访问脚本属性
任何定义的脚本属性都作为存储的成员在self中可用,self是脚本实例引用:
-- my_script.script
go.property("my_property", 1)
function update(self, dt)
-- 读取和写入属性
if self.my_property == 1 then
self.my_property = 3
end
end
用户定义的脚本属性也可以通过get、set和animate函数访问,与任何其他属性一样:
-- another.script
-- 将"myobject#script"中的"my_property"增加1
local val = go.get("myobject#my_script", "my_property")
go.set("myobject#my_script", "my_property", val + 1)
-- 为"myobject#script"中的"my_property"创建动画
go.animate("myobject#my_script", "my_property", go.PLAYBACK_LOOP_PINGPONG, 100, go.EASING_LINEAR, 2.0)
工厂创建的对象
如果您使用工厂创建游戏对象,可以在创建时设置脚本属性:
local props = { health = 50, target = msg.url("player") }
local id = factory.create("#can_factory", nil, nil, props)
-- 访问工厂创建的脚本属性
local url = msg.url(nil, id, "can")
local can_health = go.get(url, "health")
当通过collectionfactory.create()生成游戏对象层次结构时,您需要将对象ID与属性表配对。这些表被放在一起并传递给create()函数:
local props = {}
props[hash("/can1")] = { health = 150 }
props[hash("/can2")] = { health = 250, target = msg.url("player") }
props[hash("/can3")] = { health = 200 }
local ids = collectionfactory.create("#cangang_factory", nil, nil, props)
通过factory.create()和collectionfactory.create()提供的属性值将覆盖原型文件中设置的任何值以及脚本中的默认值。
如果附加到游戏对象的几个脚本组件定义了相同的属性,每个组件都将使用提供给factory.create()或collectionfactory.create()的值进行初始化。
资源属性
资源属性的定义与基本数据类型的脚本属性类似:
go.property("my_atlas", resource.atlas("/atlas.atlas"))
go.property("my_font", resource.font("/font.font"))
go.property("my_material", resource.material("/material.material"))
go.property("my_texture", resource.texture("/texture.png"))
go.property("my_tile_source", resource.tile_source("/tilesource.tilesource"))
当定义资源属性时,它会像任何其他脚本属性一样显示在Properties视图中,但作为文件/资源浏览器字段:
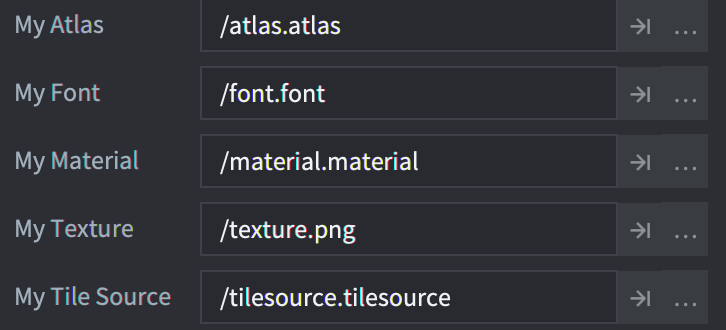
您可以使用go.get()或通过self脚本实例引用并使用go.set()来访问和使用资源属性:
function init(self)
go.set("#sprite", "image", self.my_atlas)
go.set("#label", "font", self.my_font)
go.set("#sprite", "material", self.my_material)
go.set("#model", "texture0", self.my_texture)
go.set("#tilemap", "tile_source", self.my_tile_source)
end
- English
- 中文 (Chinese)
- Español (Spanish)
- Français (French)
- Νεοελληνική γλώσσα (Greek)
- Italiano (Italian)
- Język polski (Polish)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Русский (Russian)
- Українська (Ukranian)
Did you spot an error or do you have a suggestion? Please let us know on GitHub!
GITHUB